Grid system
Bootstrap 5 Grid system
Bootstrap grid is a powerful system for building mobile-first layouts. It's very extensive tool with a great number of options. Below we present you the core knowledge. It's a simplified overview of the most commonly used examples.
Basic example
Bootstrap’s grid system uses a series of containers, rows, and columns to layout and align content. It’s built with flexbox and is fully responsive. Below is an example and an in-depth explanation for how the grid system comes together.
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col-md">
One of three columns
</div>
<div class="col-md">
One of three columns
</div>
</div>
</div>
The above example creates three equal-width columns across all devices and viewports using our
predefined grid classes. Those columns are centered in the page with the parent
.container.
Taking it step by step:
Container
Bootstrap requires a containing element to wrap site contents and house our grid system. Without a container, the grid won't work properly.
Row
Rows create horizontal groups of columns. Therefore, if you want to split your layout
horizontally, use .row.
Columns
Bootstrap's grid system allows up to 12 columns across the page.
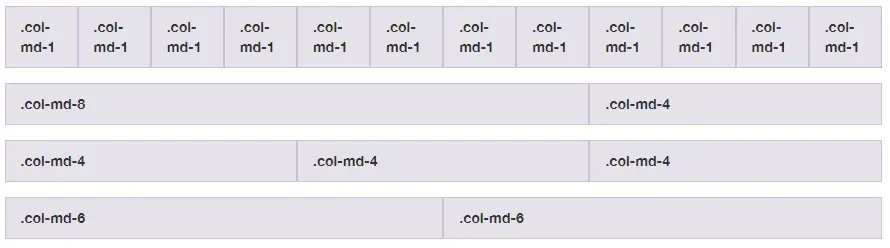
We use .col-md-* to create a column , where * specifies
the number of columns between 1 and 12.
md specifies the breakpoint where the columns change its width.
md means "screen ≥768px", so I'm the example below the columns will stretch to
100% of the width on the screens smaller or equal 768px.
How it works
Breaking it down, here’s how the grid system comes together:
-
Our grid supports six responsive breakpoints. Breakpoints are based on
min-widthmedia queries, meaning they affect that breakpoint and all those above it (e.g.,.col-sm-4applies tosm,md,lg,xl, andxxl). This means you can control container and column sizing and behavior by each breakpoint. -
Containers center and horizontally pad your content. Use
.containerfor a responsive pixel width,.container-fluidforwidth: 100%across all viewports and devices, or a responsive container (e.g.,.container-md) fir combination of fluid and pixel widths. -
Rows are wrappers for columns. Each column has horizontal
padding(called a gutter) for controlling the space between them. Thispaddingis then counteracted on the rows with negative margins to ensure the content in your columns is visually aligned down the left side. Rows also support modifier classes to uniformly apply column sizing and gutter classes to change the spacing of your content. -
Columns are incredibly flexible. There are 12 template columns available per row, allowing you to create different combinations of elements that span any number of columns. Column classes indicate the number of template columns to span (e.g.,
col-4spans four).widths are set in percentages so you always have the same relative sizing. -
Gutters are also responsive and customizable. Gutter classes are available across all breakpoints, with all the same sizes as our margin and padding spacing. Change horizontal gutters with
.gx-*classes, verical gutters with.gy-*, or all gutters with.g-*classes..g-0is also availble to remove gutters. -
Sass variables, maps, and mixins power the grid. If you don’t want to use the predefined grid classes in Bootstrap, you can use our grid’s source Sass to create your own with more semantic markup. We also include some CSS custom properties to consume these Sass variables for even greater flexibility for you.
Most common examples
A few of the most common grid layout examples to get you familiar with building within the Bootstrap grid system.
Five grid tiers
There are five tiers to the Bootstrap grid system, one for each range of devices we support. Each tier starts at a minimum viewport size and automatically applies to the larger devices unless overridden.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">.col-4</div>
<div class="col-4">.col-4</div>
<div class="col-4">.col-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-4">.col-sm-4</div>
<div class="col-sm-4">.col-sm-4</div>
<div class="col-sm-4">.col-sm-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-4">.col-lg-4</div>
<div class="col-lg-4">.col-lg-4</div>
<div class="col-lg-4">.col-lg-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xl-4">.col-xl-4</div>
<div class="col-xl-4">.col-xl-4</div>
<div class="col-xl-4">.col-xl-4</div>
</div>
Three equal columns
Get three equal-width columns starting at desktops and scaling to large desktops. On mobile devices, tablets and below, the columns will automatically stack.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
</div>
Three unequal columns
Get three columns starting at desktops and scaling to large desktops of various widths. Remember, grid columns should add up to twelve for a single horizontal block. More than that, and columns start stacking no matter the viewport.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3">.col-md-3</div>
<div class="col-md-6">.col-md-6</div>
<div class="col-md-3">.col-md-3</div>
</div>
Two columns
Get two columns starting at desktops and scaling to large desktops.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8">.col-md-8</div>
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
</div>
Two columns with two nested columns
Per the documentation, nesting is easy—just put a row of columns within an existing column. This gives you two columns starting at desktops and scaling to large desktops, with another two (equal widths) within the larger column.
At mobile device sizes, tablets and down, these columns and their nested columns will stack.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8">
<div class="pb-3">
.col-md-8
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">.col-md-6</div>
<div class="col-md-6">.col-md-6</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
</div>
Mixed: mobile and desktop
The Bootstrap v5 grid system has five tiers of classes: xs (extra small, this class infix is not used), sm (small), md (medium), lg (large), and xl (extra large). You can use nearly any combination of these classes to create more dynamic and flexible layouts.
Each tier of classes scales up, meaning if you plan on setting the same widths for md, lg and xl, you only need to specify md.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8">.col-md-8</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-6 col-md-4">.col-6 .col-md-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6">.col-6</div>
<div class="col-6">.col-6</div>
</div>
Mixed: mobile, tablet, and desktop
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-6 col-lg-8">.col-sm-6 .col-lg-8</div>
<div class="col-6 col-lg-4">.col-6 .col-lg-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6 col-sm-4">.col-6 .col-sm-4</div>
<div class="col-6 col-sm-4">.col-6 .col-sm-4</div>
<div class="col-6 col-sm-4">.col-6 .col-sm-4</div>
</div>
Containers
Additional classes added in Bootstrap v5 allow containers that are 100% wide until a particular breakpoint.
<div class="container">.container</div>
<div class="container-sm">.container-sm</div>
<div class="container-md">.container-md</div>
<div class="container-lg">.container-lg</div>
<div class="container-xl">.container-xl</div>
<div class="container-xxl">.container-xxl</div>
<div class="container-fluid">.container-fluid</div>
